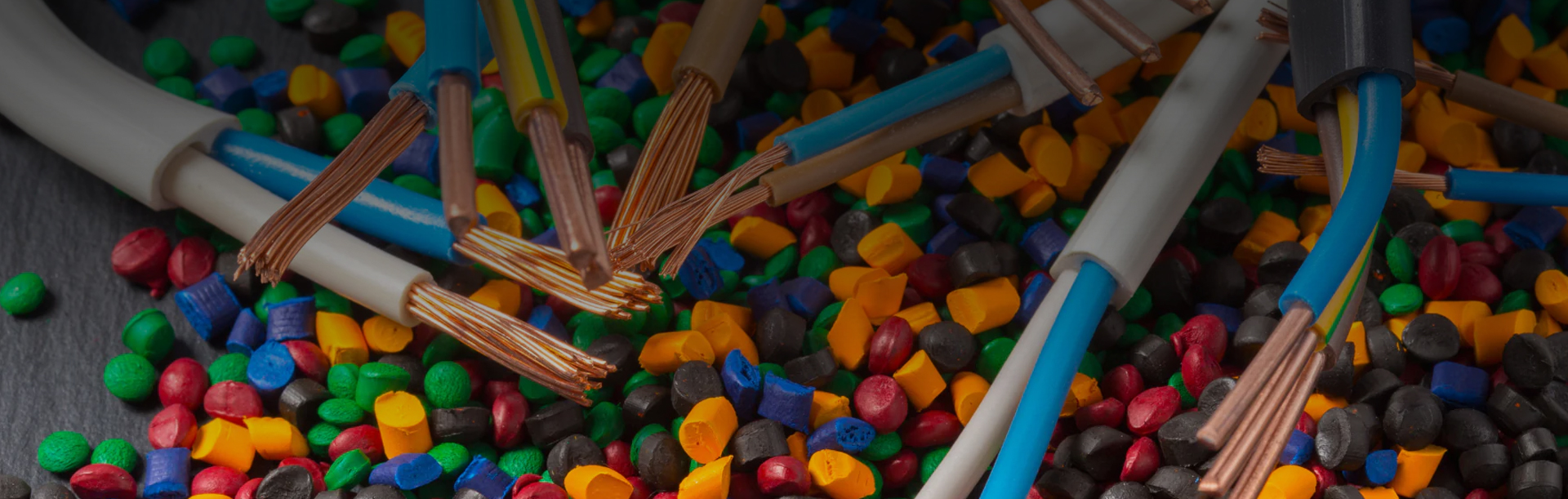
ULJ-105 UL Standard 105℃ Polyvinyl Chloride Insulation Compound has heat resistance and can work sta...
ABOUT US
30YEARS OF
EXPERIENCE
About Us
Coming From China, Marketing To The World.
Hangzhou Meilin New Materials Technology Co., Ltd. is China Custom Electronic Wire Compound Manufacturers and Electronic Wire Compound ODM/OEM Exporters, we were established in July 1994 (formerly known as Zhejiang Lin'an Hongyan Plastic Factory). The company has two factories located at 619 Linglongshan Road and 259 Xingyu Street, Lingqiu Street, Linglong Industrial Park, Lin'an District, Hangzhou City. The registered capital of the company is 75 million yuan, covering an area of over 18000 square meters and a building area of over 30000 square meters. Currently, modern industrial factories and 18 advanced automated production lines have been built. The new factory area will be produced in 2021, making it the cleanest and most beautiful professional cable material manufacturer in the entire region—agreement conditions.
-
admin 19 Dec 2024
How to use Medical Polyvinyl Chloride Compound to improv...
Read MoreThe key to improving the performance of single-use medical products with Medical Polyvinyl Chloride Compound is to enhance their physical, chemical and biological properties through formulation improv...
-
admin 12 Dec 2024
How does flame-retardant PVC cable material improve the ...
Read MoreFlame-retardant PVC cable material can effectively improve the safety and fire resistance of cables through its unique formula and chemical composition, which is specifically reflected in the followin...
-
admin 05 Dec 2024
How do PVC sheath plastic compounds help cables cope wit...
Read MorePVC (polyvinyl chloride) sheath plastic compounds are widely used for the outer protection of electrical cables because of their superior physical properties and durability, making them an ideal choic...
-
admin 28 Nov 2024
Understanding Insulation Cable Compounds: Types, Propert...
Read MoreAn insulation cable compound is a material that surrounds the conductors within a cable to provide electrical insulation. This compound acts as a barrier to prevent the flow of electrical currents out...
Cable Compound For Electronic Appliances Industry Knowledge
What key performance indicators should be considered when selecting composite materials for electronic cables?
When selecting composite materials for electronic cables, the following key performance indicators are very important:
Electrical performance:
Dielectric Constant: affects the capacitance and signal transmission speed of the material.
Dielectric Loss: affects the efficiency of signal transmission, especially in high-frequency applications.
Insulation Resistance: ensures that current does not leak through the insulation layer, affecting the reliability of the cable.
Thermal performance:
Thermal Stability: the performance of the material in a high temperature environment, including thermal decomposition temperature and thermal expansion coefficient.
Heat Resistance: the long-term stability of the material at high temperatures to avoid performance degradation or failure in a hot environment.
Mechanical properties:
Flexibility: the performance of the material when bent and twisted, affecting the laying and service life of the cable.
Tensile Strength: the load-bearing capacity of the material during stretching, ensuring that it is not easy to break under mechanical stress.
Abrasion Resistance: the ability to resist external physical damage and extend the service life of the cable.
Chemical stability:
Corrosion Resistance: The material's resistance to chemicals and environmental conditions, especially in harsh environments.
Oil and Solvent Resistance: Resistance to common chemicals and solvents.
Flammability:
Flammability Rating: The material's burning characteristics when exposed to flames, ensuring safety.
Environmental adaptability:
UV Resistance: The material's resistance to ultraviolet rays, suitable for outdoor or high-intensity light environments.
Moisture Resistance: The material's resistance to moisture and water, preventing the degradation of insulation performance.
How do composite materials for electronic cables perform in terms of high temperature resistance and chemical corrosion resistance?
The performance of composite materials for electronic cables in terms of high temperature resistance and chemical corrosion resistance varies depending on the type of material. The following are the performances of several common composite materials for electronic cables in these aspects:
1. Polyurethane (PU)
High temperature resistance: Polyurethane has average high temperature resistance and can usually maintain its performance in the range of 80°C to 120°C. Performance degradation or deformation may occur above this temperature.
Chemical corrosion resistance: It has good resistance to most chemicals, but may be corroded in strong acids, strong alkalis and certain solvents.
2. Silicone
High temperature resistance: Silicone has excellent high temperature resistance and can usually withstand ambient temperatures of up to 200°C or even 250°C. Some special silicones can withstand higher temperatures.
Chemical corrosion resistance: Silicone has good resistance to most chemicals and solvents, but has limited resistance to strong acids and alkalis.
3. Fluoropolymer
High temperature resistance: Fluoropolymers have excellent high temperature resistance and can usually maintain stable performance in environments above 260°C.
Chemical corrosion resistance: Fluoropolymers have extremely high tolerance to almost all chemicals, including strong acids, strong bases and organic solvents.
4. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE, Teflon)
High temperature resistance: PTFE has excellent high temperature resistance and can withstand ambient temperatures up to 260°C and remain stable for a long time.
Chemical corrosion resistance: PTFE has excellent corrosion resistance to almost all chemicals, including strong acids, strong bases and organic solvents.
5. Polyethylene (Polyethylene, PE)
High temperature resistance: Polyethylene has poor high temperature resistance and can generally be used in the range of 70°C to 90°C. Exceeding this temperature may cause deformation or melting.
Chemical corrosion resistance: It has good tolerance to most chemicals, but performs poorly in strong acid and strong base environments.
6. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
High temperature resistance: PVC has average high temperature resistance, usually working stably in an environment of 70°C to 85°C. It will soften and lose strength above this temperature.
Chemical corrosion resistance: PVC has good resistance to most chemicals, but may degrade in some strong acid and alkali environments.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体 русский
русский















